The Latest Updates on Tax Evasion Laws—The UAE Ministry of Finance has issued new administrative penalties for violations, Cabinet Decision No. (75) of 2023 related to the Federal Decree-Law No. 47 of 2022 on the Taxation of Corporations and Businesses (Corporate Tax Law). The penalties, which take effect on August 1, 2023, are designed to ensure compliance with the new tax law and to deter non-compliance. The penalties apply to both individuals and businesses that fail to meet their obligations under the Corporate Tax Law.
The penalties range from a minimum of AED 5,000 to a maximum of AED 1 million, depending on the severity of the violation. In addition, the Federal Tax Authority may impose additional penalties, such as interest on unpaid taxes or the denial of tax deductions or exemptions.
In addition, individuals who have committed specific tax crimes under Article 25(4) of the Decree-Law, including tax evasion, facilitation, or concealment, must have a payment of AED 50,000 prior to the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) will reconcile with them. Reconciliation is contingent on the fulfillment of all of these requirements.
“Adhering to Corporate Tax compliance is a responsibility of all taxable persons to support the implementation of the Corporate Tax system in the UAE, which is in line with the highest global standards. It also drives sustainable economic growth in the UAE by providing a conducive legislative environment that promotes tax compliance.”
Undersecretary, Ministry of Finance
Period of Record Keeping
The UAE Federal Tax Authority (FTA) has issued new regulations governing the period of time that businesses must retain their accounting records, commercial books, documents, and information. Therefore, these regulations are designed to ensure that businesses have the necessary records to comply with their tax obligations and to facilitate tax audits by the FTA.
The retention periods for different types of records vary depending on the nature of the record and the purpose for which it is being retained. For example, records related to real estate transactions must be retained for a period of seven years, while records related to employee payroll must be retained for a period of five years.
In addition to the general retention periods, records that are relevant to voluntary disclosures are also subject to extended retention periods. Taxpayers who make voluntary disclosures to the FTA of errors or omissions in their tax returns must retain records relevant to the disclosure for a period of six years after the end of the tax period to which they relate.
The Reconciliation Process
Individuals who have committed tax evasion crimes can submit a reconciliation application to the FTA before a criminal case is initiated. The application must include a payment of AED 50,000 and the full amount of payable tax and administrative penalties. Upon acceptance, a record of reconciliation will be issued. This record will be a valid defense in any criminal proceedings related to the tax crimes that were the subject of the reconciliation.
The amount required for reconciliation may vary depending on the stage of the criminal case and the nature of the tax crime. In all cases, reconciliation requires settling the full amount of payable tax and administrative penalties, as well as an additional amount calculated as a percentage of the tax evaded.
This new reconciliation process provides a way for individuals who have committed tax evasion crimes to avoid criminal prosecution and the associated penalties. However, it is important to note that the latest updates on tax evasion laws amount required for reconciliation may be significant, and it is not guaranteed that the application will be accepted.
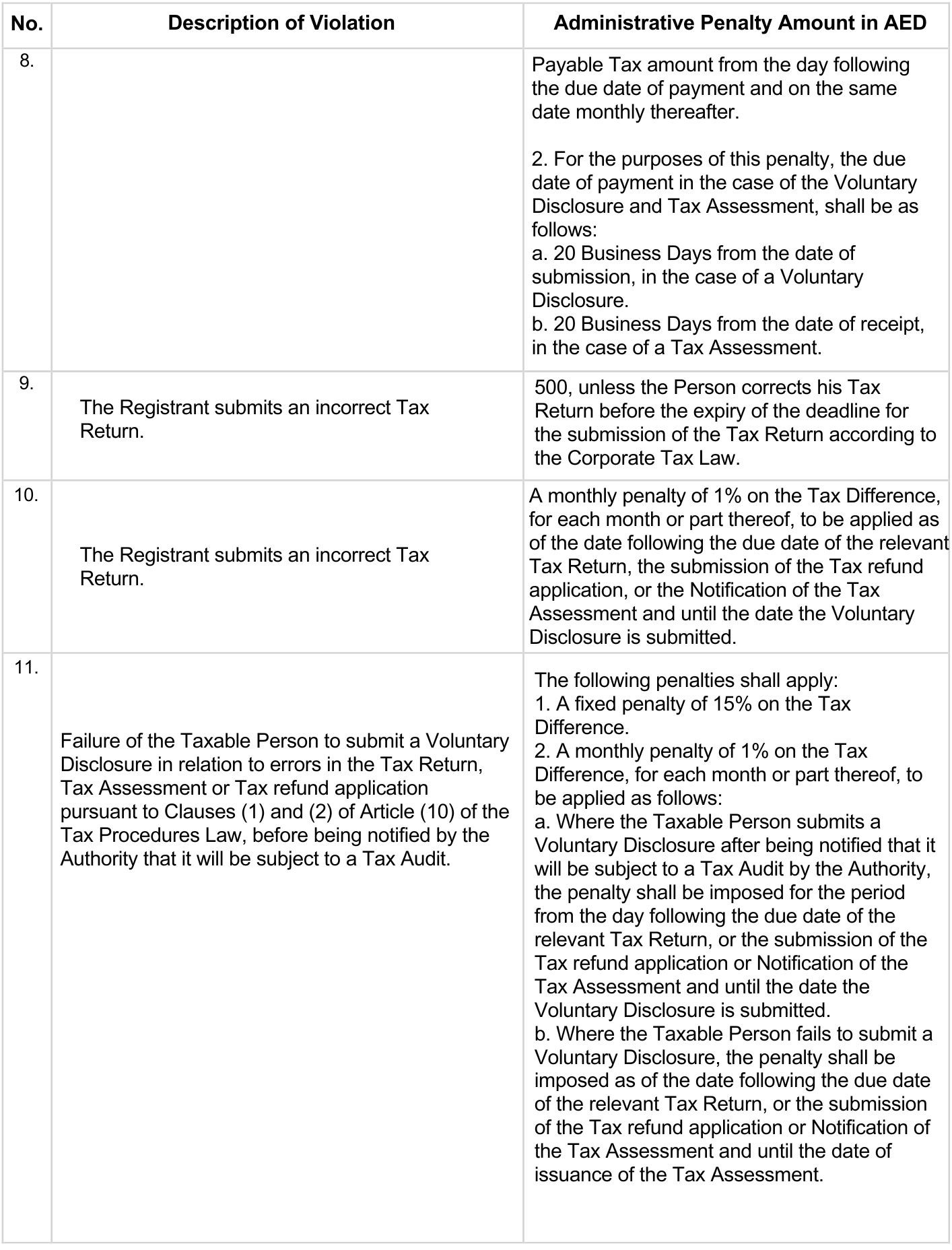
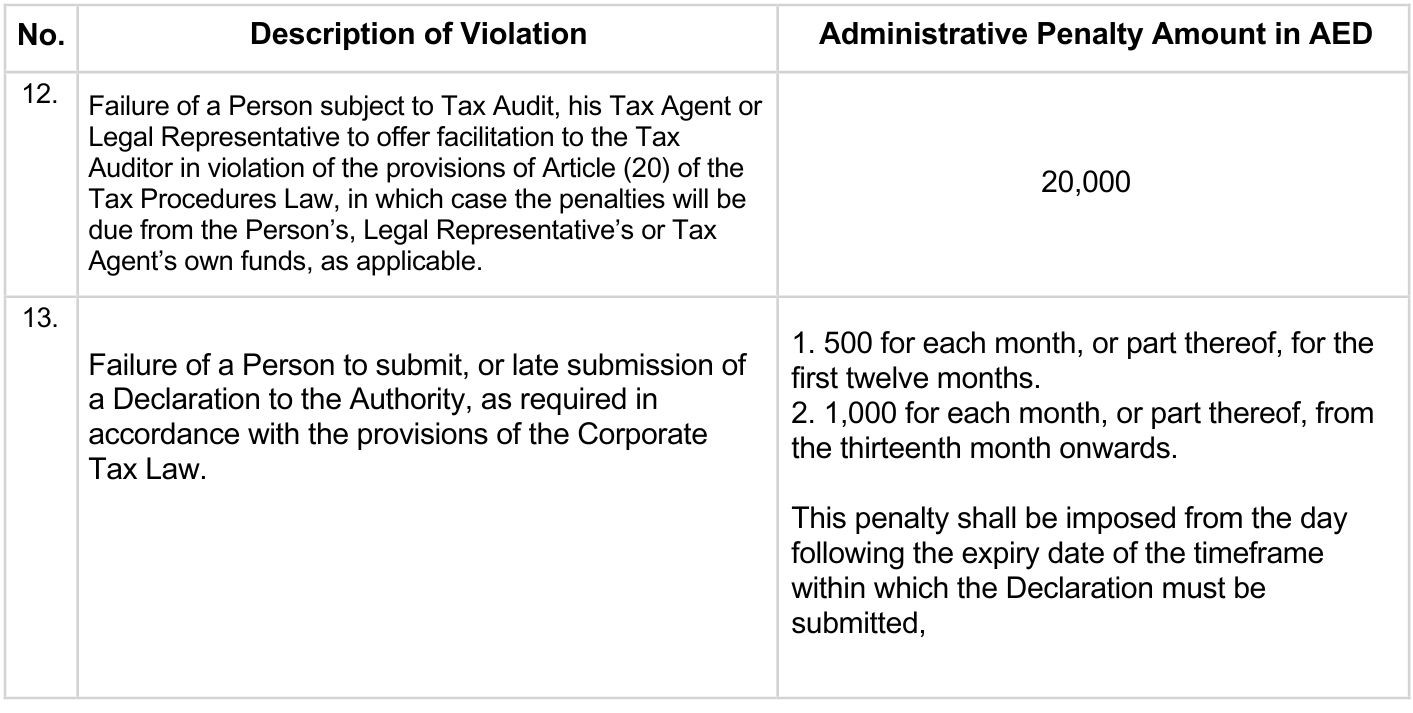
There are other potential infractions that may be subject to administrative action: